Flower differentiation and fruiting dynamics in olive trees (Olea europaea): Eco-physiological analysis in the Mediterranean basin
Published 2022-01-26
Keywords
- Anthesis,
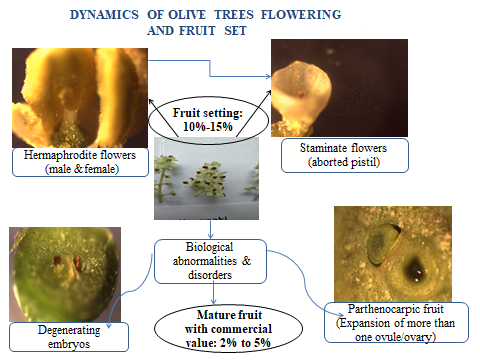
- fruit setting,
- hermaphrodite and staminate flower,
- olive,
- pistil abortion
How to Cite
Abstract
The formation of flowers in sufficient number and quality is a prerequisite for a successful subsequent fruit set. Despite the abundant flowering, olive trees (Olea europea) are characterized by a very low fruit set, and a very severe yield alteration leading to market fluctuation over time. The goal of this paper is to explore and analyze eco-physiological driving factors behind the poor fruit set in Mediterranean olive groves. The key mechanisms causing floral differentiation and extreme yield alternate are functional of plant genetic variability, nutrient competition, and some ecological aspects as a response to climate change. Additionally, olive inflorescence architecture appears to be complex and can vary between cultivars; the olive flower differentiation results in a variable proportion of hermaphrodite, pistillate and staminate flowers among olive cultivars as well as across canopy positions and branches, enhancing nutrient competition between flowers. Self-pollination could be one of the limiting factors for increasing early fruit abscission and extreme alternate fruit-bearing. Hormonal treatments to reduce alternate production in olive trees should be explored. The current review analysis shall help to improve olive grove management, but also for breeding new cultivars more suitable for Mediteranean agro-ecological constraints. Ovule viability and fertilisation, and embryo sac development abnormalities should all be further investigated.





