Maintaining postharvest quality of bell pepper (Capsicum annuum L. cv. California Wonder) using cactus (Opuntia stricta L.) mucilage coating
Published 2022-07-05
Keywords
- Ascorbic acid content,
- edible coating,
- fresh weight loss,
- fruit vegetable,
- shelf life
How to Cite
Funding data
Abstract
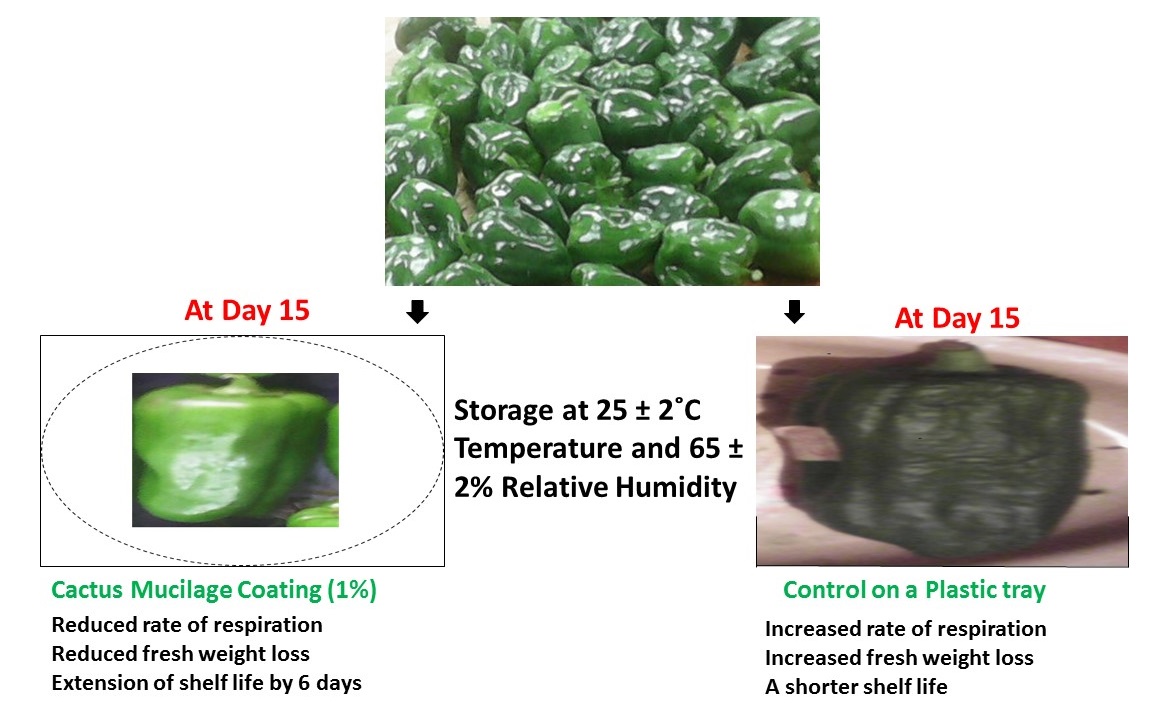
Bell pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) experiences significant qualitative and quantitative loss during postharvest. This study aimed at providing an alternative postharvest handling technology for bell pepper. The factor studied was cactus (Opuntia stricta L.) mucilage coating at four levels: 0% (distilled water), 1, 2, and 3%. The fruits were stored under ambient conditions (25 ± 2°C temperature and 65 ± 2% relative humidity) until senescence. Weight loss and total soluble solids content were determined at an interval of 3 days whereas iron and ascorbic acid content were determined at an interval of 4 days. Shelf life elapsed when fruit lost 25% of their initial weight on average. Cactus mucilage coating reduced weight loss by up to 21.64%, maintained total soluble solids by up to 14.93%, iron by up to 6.46%, ascorbic acid by up to 19.46% and extended shelf life by up to 6 days. Cactus mucilage coating at 1% was the best treatment and therefore can be used by bell pepper growers, retailers, and consumers to maintain postharvest quality and extend shelf life of bell pepper.





