Fruit maturity and antioxidant activity affecting superficial scald development in ‘Abate Fétel’ pears
Published 2023-05-10
Keywords
- Antioxidant capacity,
- fruit quality,
- preharvest factors,
- Pyrus communis,
- superficial scald
- total phenolic content ...More
How to Cite
Copyright (c) 2023 Alessandro Bonora, Anna Venturoli, Melissa Venturi, Alexandra Boini, Luca Corelli Grappadelli

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Abstract
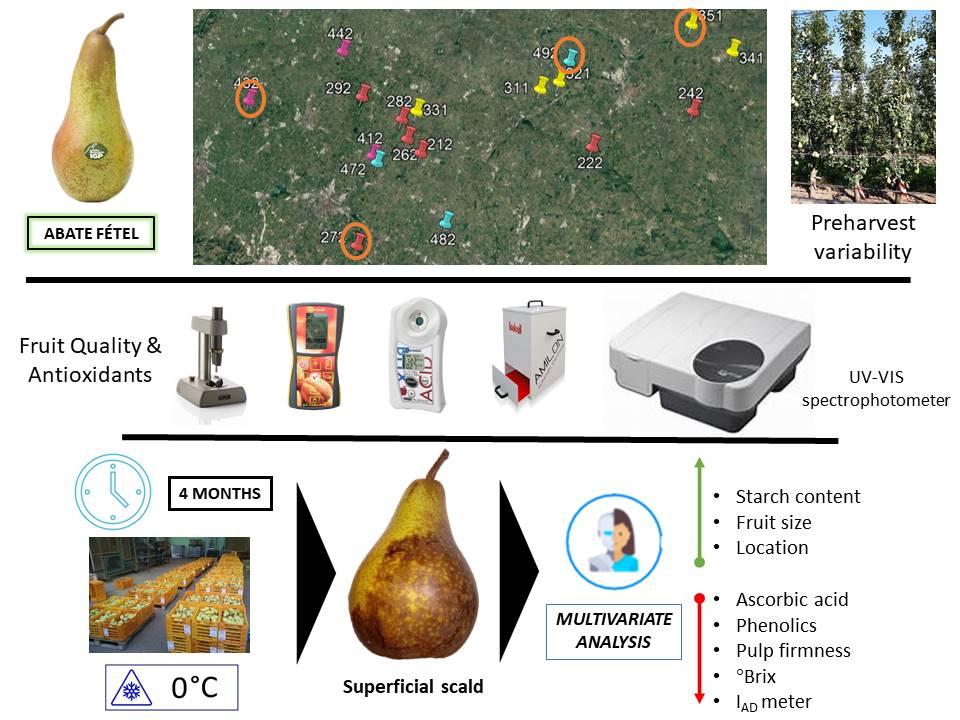
Superficial scald (SS) is one of the main physiological disorders affecting postharvest of pears. Its onset is linked to oxidative processes. Antioxidant compounds such as ascorbic acid and phenolics could play a key role in preventing SS. Growing environment and fruit quality also have an influence on SS symptoms occurrence. The aim of this project is to understand the relationship between antioxidant activity, phenolic content, and development of SS in ‘Abate Fétel’ pear. Moreover, the effect on SS of fruit maturity at harvest was assessed using multivariate statistical approach. Data were collected in thirty orchards in the Emilia-Romagna region (Italy) in three seasons (2018, 2019 and 2020), and the fruit were stored in a regular atmosphere for 120 days. Antioxidant capacity was determined by 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazy (DPPH) method and total phenol content by Folin-Ciocalteau colorimetric protocol. The results showed that 340 mg of ascorbate/100 g of FW and 300 mg of gallic ac./100 g of FW at least provide good protection against SS. Multivariate analysis indicated that pulp firmness and index of absorbance difference ( lAD ) seem to keep low the SS occurence, when at harvest are higher than 6.3 kg and 1.9, respesctively. In conclusion, it would be possible to build a forecasting model to control SS that considers pre-harvest data and content of antioxidants in different orchards, to improve the postharvest management of ‘Abate Fétel’.





