Field evaluation of biostimulants on growth, flowering, yield, and quality of snap beans in subtropical environment
Published 2024-07-01
Keywords
- Chitosan,
- potassium silicate,
- 6-benzylaminopurine,
- snap bean,
- triacontanol
How to Cite
Copyright (c) 2024 Ibrahim Abouelsaad

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Abstract
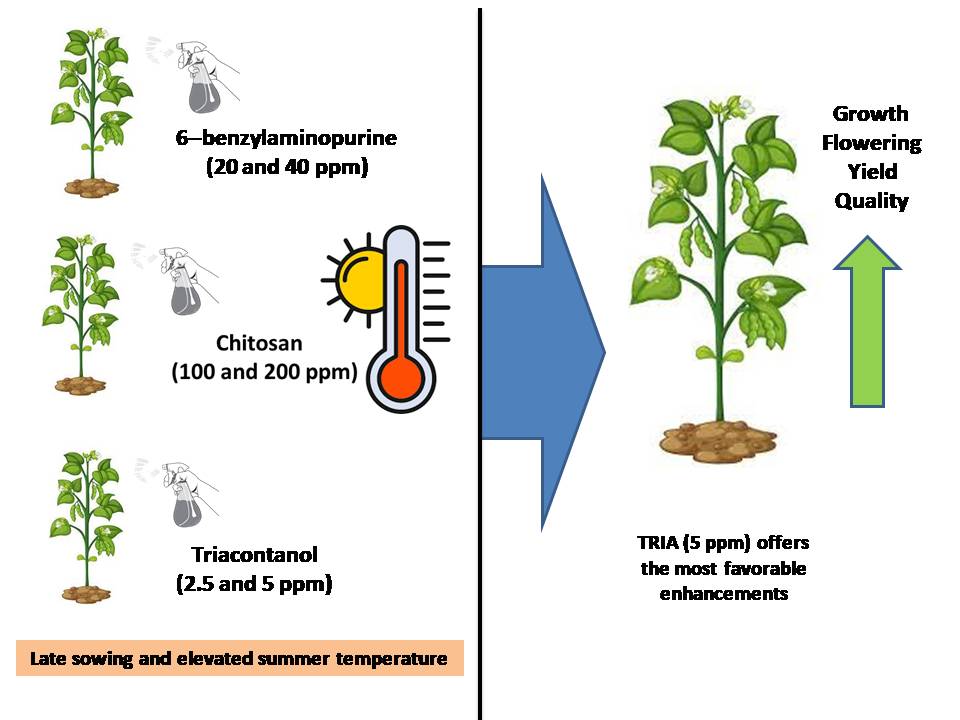
The cultivation of snap beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in subtropical regions faces environmental challenges leading to potential declines in yield. This study explores the efficacy of biostimulants as a solution, specifically investigating spraying treatments with 6-benzylaminopurine (6-BA), chitosan (Ch), triacontanol (TRIA), and potassium silicate (KSi) on the snap bean cv. Paulista. Over two growing seasons with late sowing and elevated summer temperatures, the research assesses growth, flowering, yield, and quality. Notably, 5 ppm TRIA demonstrates the most significant impact on plant growth and leaf nutrient content. Treatments with 40 ppm 6-BA, 5 ppm TRIA, or 200 ppm KSi exhibit notable effects on inflorescence flower count and flowers per plant. These treatments prove most effective for crucial green pod yield measures, including the number and weight of marketable pods. Moreover, 40 ppm 6-BA or 5 ppm TRIA significantly enhances pod characteristics, such as length, diameter, and weight, consistently improving over both seasons. Particularly, 5 ppm TRIA outperforms in enhancing the chemical quality of pods throughout the study. Overall, the findings suggest that the application of 5 ppm TRIA offers the most favorable enhancements for the growth, flowering, productivity, and quality of snap bean plants in subtropical field conditions.




