Evaluation of Hemerocallis germplasm using single nucleotide polymorphisms of nrITS and chloroplast interspacer region
Published 2022-10-04
Keywords
- Daylily,
- haplotype,
- nocturnal flowering,
- polymerase chain reaction,
- sequence analysis
How to Cite
Copyright (c) 2022 Mark Roh, Seo Young Park, Young Hee Joung, Jeung Keun Suh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Abstract
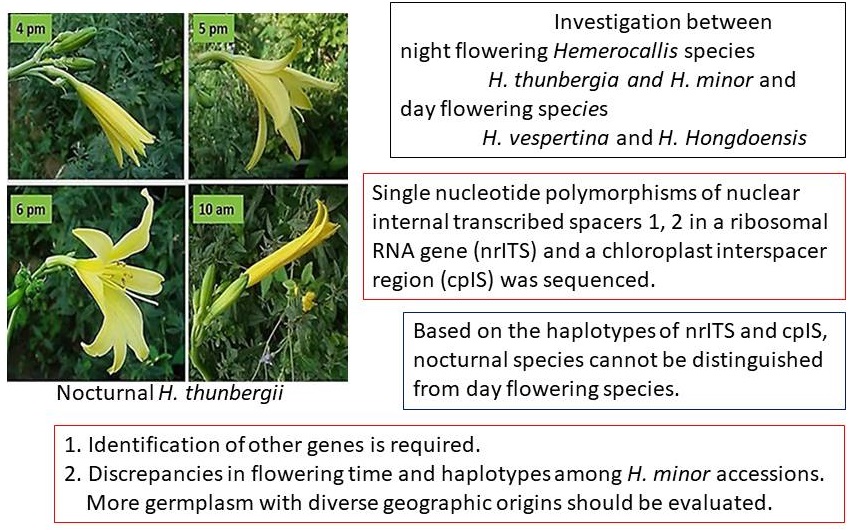
This study was initiated to distinguish nocturnal (night) flowering Hemerocallis species from day flowering species based on the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of nuclear internal transcribed spacers 1, 2 in a ribosomal RNA gene (nrITS) and a chloroplast interspacer region (cpIS). Four nocturnal flowering species, H. citrina, H. thunbergii, H. minor, and H. lilioasphodelus, were collected including Korea, and compared with day flowering species that included H. vespertina and H. hongdoensis. Based on the haplotypes of nrITS and cpIS, nocturnal species cannot be distinguished from day flowering species. Discrepancies in flowering time and haplotypes among H. minor accessions suggest that more germplasm with diverse geographic origins should be evaluated and identification of other genes is required to effectively distinguish nocturnal species from day flowering species.




