Inhibition of bleaching of stored red hot pepper through appropriate postharvest technologies and practices
Published 2024-07-01
Keywords
- Capsicum spp.,
- carotenoids,
- color fading
How to Cite
Copyright (c) 2024 Obse Fikiru Etefa, Sirawdink Fikreyesus Forsido, Yetenayet B. Tola

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Abstract
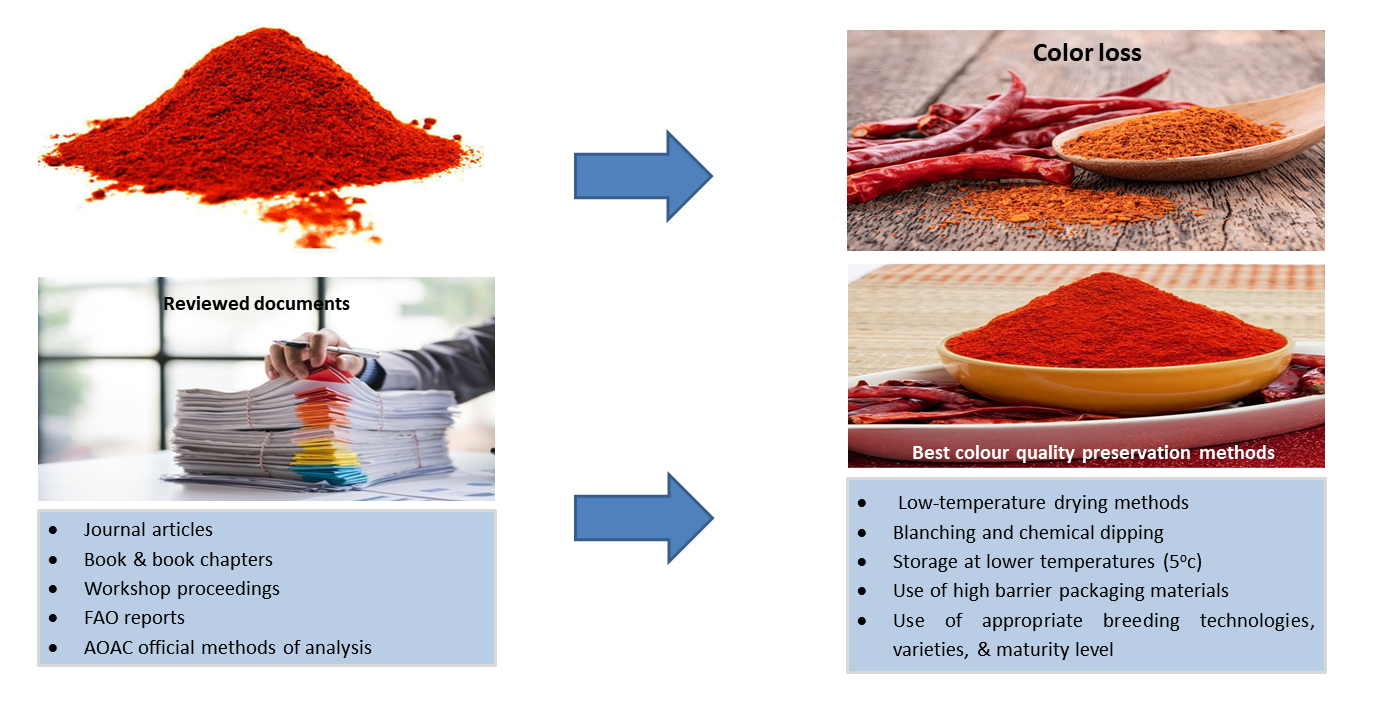
The colour qualities of hot red pepper are the major issue in pepper value chain. Due to poorly coordinated scientific evidence, information on the factors causing colour loss and the inhibition mechanism is not well known. Therefore, this review paper aimed to summarize the inhibition mechanism of stored red hot pepper bleaching through appropriate postharvest technologies and practices. The information in this paper was gathered from a variety of sources, including journal articles, books, book chapters, workshop proceedings, FAO reports, and AOAC official methods of analysis. According to these studies, carotenoids, surface colour, and extractable colour (ASTA value) are the primary colourants that define hot red pepper. The findings demonstrate that low-temperature drying methods, such as open sun drying, are best for preserving the red hot pepper powder’s colour quality, while higher temperatures cause the colour to darken. Blanching, the use of desiccants (CaCl2), and chemical dipping are pretreatments that preserve the best colour quality by hastening the drying time. Similarly, storage of red hot pepper powder at lower temperatures (5oC) resulted in less colour degradation. In other words, materials used for packaging that have a high barrier to light, moisture, and air, such as laminated aluminium, amber or black polyethylene, and high-density polyethylene, maintained a higher level of colour quality. Through their influence on drying and processing times, breeding technologies, varieties, and maturity level also impact colour quality. In conclusion, the colour quality of red hot pepper is highly influenced by environmental, biological, and processing methods. It is, therefore, critical to use appropriate drying and pretreatment techniques, storage time, well-managed storage temperature, appropriate processing methods and packing materials, and improved agronomic practices for the sustainable management of colour fading and adulteration that can occur throughout the value chain.




