Published 2020-04-01
Keywords
- antioxidant capacity,
- chemical AgNPs,
- germination value,
- green AgNPs,
- liquid peroxidation
- phenol,
- protein ...More
How to Cite
Abstract
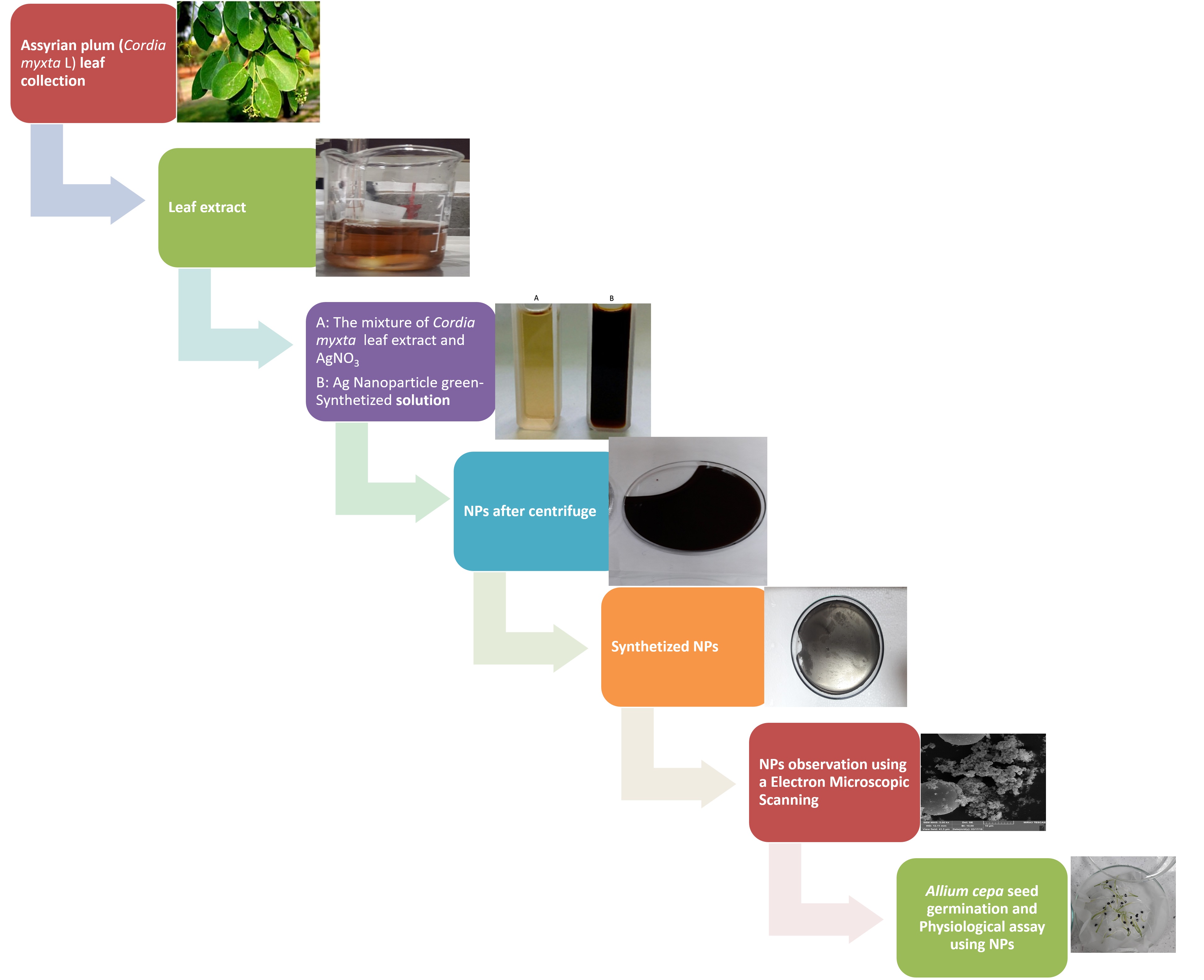
Plant-mediated nanoparticles synthesis is considered as one of the appealing options in bio-nanoparticles synthesis, however, there is contradictory information about the positive or negative impacts of nanoparticles on plants. Investigating the toxic effects of Ag NPs on model plants, such as onion, can reveal the probability of damage. Thus, the present study was conducted to compare the germination indices and biochemical parameters of edible onion seeds treated with different concentrations of two types of silver nanoparticles (green synthesized and chemical synthesized) to examine the oxidative stress. Based on our results, the interaction between leaf extract and silver salt resulted in a color change from pale yellow to dark brown, the first sign of the AgNPs formation. The green AgNPs treatment improved the onion germination indices. The green AgNPs-exposed seeds displayed a no-significant reduction in protein content and same protease activity as the control treatment, but chemical AgNPs-treated displayed a significant rise of protease and reduction in protein content in concentration more than 0.06 gL-1. In chemical AgNPs-treated seeds both peroxidase and catalase displayed an ascending linear trend and the most activities belonged to chemical AgNPs at 0.05 g L-1 (315.62 and 51.45 μmol min-1g-1 FW, respectively). Both nanoparticle types made an increase in MDA, but green AgNPs did not significantly differ with control treatment. It can be concluded that the green synthesis of nanoparticles is a safe and suitable alternative for chemical-synthesized metal nanoparticles.





