Published 2022-04-22
Keywords
- Italian MPs,
- Italian Public Opinion,
- EU attitudes,
- Euroscepticism,
- Populism
- Survey ...More
How to Cite
Funding data
-
Sapienza Università di Roma
Grant numbers Unitelma 2018 Reserch Grant
Abstract
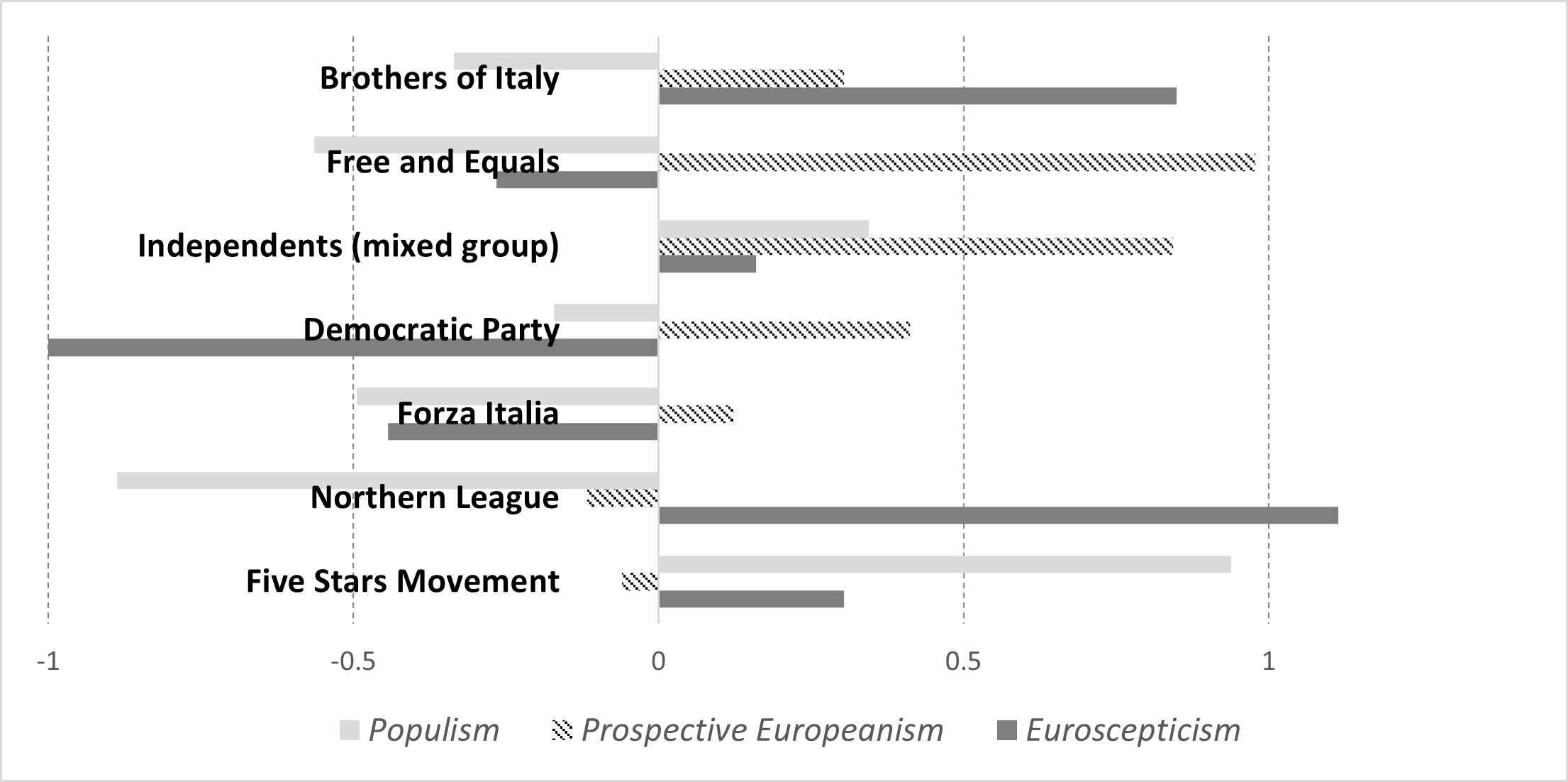
The recent history of European politics has been characterised by the mounting phenomena of populism and Euroscepticism. Some recent analyses discuss the possible convergence between the two, exemplified, above all, by the increased success of Eurosceptic and populist parties. Conceptually and historically, Euroscepticism and populism are two distinct ideological realms. To what extent do they develop in parallel or converge, both at the elite and mass levels? We address this question by looking at the Italian case, where populism and Euroscepticism have apparently progressed simultaneously. Through an analysis of the attitudes of political elites and the public, we argue that the two phenomena actually move in parallel and in general do not converge, with the main exception of the Five Star Movement where a convergence is instead visible. Finally, by observing the effects of Euroscepticism and populism on the voting choices of citizens, we find a high level of congruence in the political system between demand and supply, hence between voters and their representatives.

